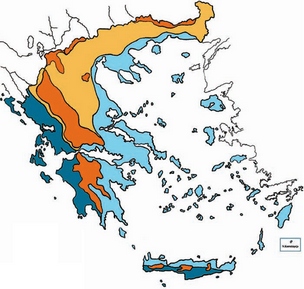
 The climate in Greece is predominately Mediterranean with mild and rainy winters and warm and dry summers. The climate of the country can be divided into four main subtypes:
The climate in Greece is predominately Mediterranean with mild and rainy winters and warm and dry summers. The climate of the country can be divided into four main subtypes:
- Wet Mediterranean (Western Greece, Western Peloponnese, semi-mountainous areas and lowlands of Epirus)
- Dry Mediterranean (Cyclades, Cretan coastline, Dodecanese, Eastern Peloponnese, Attica, Eastern Central Greece lowlands)
- Continental (Western Macedonia, interior highlands of Continental Greece, northern Evros)
- Alpine (mountain areas with an altitude of approximately > 1,500 metres in Northern Greece, > 1,800metres in Central Greece and> 2,000metres in Crete).
Temperatures are rarely excessive in coastal areas. The largest temperature range is observed in enclosed inland plains and the highlands of the country, both on an annual and daily basis. Snowfall is common on the mountains from the end of September (in northern Greece, late October on average in the rest of the country), while in the lowlands it snows mainly from December to mid-March. In Florina, however, it has snowed even in May. In the coastal areas of islands snowfall rarely occurs and it is not a key feature of the climate. The heat waves mainly affect the lowlands and are more frequent in July and August. However, they rarely last for more than 3 days.
In terms of climate, the year can be divided mainly into two seasons: The cold and rainy period, which lasts from mid-October until the end of March, and the warm and dry season, which lasts from April to October.
During the first period the coldest months are January and February where the average mean minimum temperature ranges between 5-10 °C in coastal areas, between 0-5 °C in continental areas and at temperatures below zero in northern regions.
Rainfall does not last many days, even during wintertime, and the sky does not remain cloudy throughout the winter, as in other regions of the world. The bad weather is occasionally interrupted by sunny days in January and the first 15 days of February, which have been known as "Halcyon days" since antiquity. During this period, therefore, in the islands, mainly in the southern part of the country, for instance in Crete, the temperature can exceed 18-20 Celsius degrees, 13-14 °C in Attica and 9 °C or even 10 °C in Thessaloniki. In other cities, such as Alexandroypoli, the temperature rises above 7-8 °C during the Halcyon days, allowing the snow to melt during the day.
Winters are milder in the Aegean and the Ionian Sea than in Northern and Eastern mainland Greece. During the warm and dry season the weather is stable, the sky is clear, the sun is bright and it does not rain except from rare intervals with showers or thunderstorms that do not last long.
The warmest period is the last ten days of July and the first ten days of August, when the average maximum temperature ranges from 30 °C to 35 °C. During the warm season the high temperatures are moderated by the cool sea breeze in the coastal areas of the country and the north winds (annual) blowing mainly in the Aegean.
Spring is short, because the winter may be late, but summer begins early. Autumn is long and warm and sometimes is extended in southern Greece and the islands until mid-December. In Athens, the capital, cold weather is usually noticeable from November onwards, and from then it continues until the end of March. After mid-December, urban areas develop particularly cold weather, which continues until the end of February. Since the first days of March spring becomes noticeable and the temperature rises gradually. The coldest time of the year in the city of Athens is considered to be from the last week of December until the third week of January. More specifically, the lowest temperature ever recorded in Athens was -17.1 °C on December 28, 1938 while the lowest observed in the country was -30 °C. -28 °C (Kato Nevrokopi) and -27 °C (Ptolemaida) have also been recorded. Greece holds the record for highest recorded temperature in Europe with 48.0 °C in Athens on July 10, 1977 - in fact it has been reported by sources that the thermometer reached 48.7 °C. This temperature was recorded on July 10, 1977 in the town of Elefsina. Other high temperatures listed are 47.5 °C in New Filadelfeia (Municipality of Athens) on 26/6/2007 and in Ilion, Attica on 26/6/2007.
| City | Annual Average | Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | Jun. | Jul. | Aug. | Sep. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. |
| Athens | 18,1 | 5,1 | 6,5 | 8,7 | 14,6 | 21,3 | 28,1 | 31,0 | 30,4 | 25,4 | 18,1 | 11,3 | 7,0 |
| Ioannina | 14,3 | 4,7 | 6,1 | 8,8 | 12,4 | 17,4 | 21,9 | 24,8 | 24,3 | 20,1 | 14,9 | 9,7 | 5,9 |
| Arta | 17,2 | 8,7 | 9,4 | 11,9 | 15,2 | 19,9 | 24,0 | 26,5 | 26,5 | 23,1 | 18,3 | 13,5 | 9,9 |
| Alexandroupoli | 15,0 | 5,0 | 5,9 | 8,3 | 13,1 | 18,3 | 23,1 | 25,8 | 25,4 | 21,1 | 15,6 | 10,8 | 7,1 |
| Kavala | 15,8 | 6,8 | 7,2 | 9,3 | 13,4 | 17,7 | 23,0 | 26,5 | 26,3 | 22,4 | 17,2 | 11,4 | 8,0 |
| Thessaloniki | 15,7 | 5,2 | 6,7 | 9,7 | 14,2 | 19,6 | 24,4 | 26,6 | 26,0 | 21,8 | 16,2 | 11,0 | 6,9 |
| Serres | 15,1 | 3,9 | 6,2 | 9,6 | 14,2 | 19,6 | 24,3 | 26,3 | 25,3 | 21,6 | 15,5 | 9,2 | 5,0 |
| Florina | 12,1 | 0,5 | 2,7 | 6,7 | 11,6 | 16,8 | 21,0 | 23,1 | 22,5 | 18,4 | 12,6 | 7,0 | 2,2 |
| Kozani | 12,9 | 2,3 | 3,7 | 6,9 | 11,6 | 16,8 | 21,5 | 24,1 | 23,6 | 19,3 | 13,5 | 8,0 | 3,9 |
| Larissa | 15,7 | 5,2 | 6,8 | 9,4 | 13,8 | 19,7 | 25,0 | 27,2 | 26,2 | 21,8 | 16,2 | 10,8 | 6,6 |
| Volos | 16,2 | 6,6 | 7,6 | 9,9 | 14,1 | 19,5 | 24,5 | 26,8 | 26,1 | 22,2 | 16,9 | 12,1 | 8,2 |
| Agrinio | 17,2 | 8,3 | 9,2 | 11,5 | 15,1 | 20,3 | 24,7 | 27,1 | 26,9 | 23,0 | 17,9 | 13,1 | 9,6 |
| Patras | 17,9 | 10,0 | 10,6 | 12,5 | 15,6 | 20,1 | 24,1 | 26,4 | 26,7 | 23,5 | 19,0 | 14,5 | 11,4 |
| Corfu | 17,5 | 9,7 | 10,3 | 12,0 | 14,9 | 19,6 | 23,9 | 26,4 | 26,3 | 22,7 | 18,4 | 14,3 | 11,1 |
| Argostoli | 18,1 | 11,5 | 11,5 | 12,9 | 15,2 | 19,4 | 23,3 | 25,5 | 25,9 | 23,4 | 19,7 | 15,7 | 12,8 |
| Chania | 18,5 | 11,6 | 11,8 | 13,2 | 16,3 | 20,1 | 24,5 | 26,5 | 26,1 | 23,3 | 19,4 | 16,1 | 13,1 |
| Elefsina | 18,3 | 9,2 | 9,7 | 11,8 | 15,9 | 21,4 | 26,1 | 28,6 | 28,2 | 24,3 | 19,0 | 14,4 | 10,9 |
| Heraklion | 18,7 | 12,1 | 12,2 | 13,5 | 16,5 | 20,3 | 24,4 | 26,1 | 26,0 | 23,5 | 20,0 | 16,6 | 13,7 |
| Kalamata | 17,8 | 10,2 | 10,6 | 12,3 | 15,2 | 19,7 | 24,1 | 26,4 | 26,3 | 23,2 | 18,9 | 14,8 | 11,7 |
| Tripoli | 14,1 | 5,1 | 5,8 | 7,9 | 11,7 | 17,0 | 22,0 | 24,5 | 24,1 | 20,0 | 14,6 | 10,1 | 6,7 |
| Lamia | 16,5 | 7,1 | 8,0 | 10,5 | 14,8 | 20,1 | 25,3 | 26,9 | 25,9 | 22,4 | 16,9 | 11,8 | 8,3 |
| Lemnos | 15,9 | 7,4 | 7,7 | 9,7 | 13,6 | 18,4 | 23,6 | 25,9 | 25,2 | 21,5 | 16,9 | 12,3 | 9,0 |
| Naxos | 18,2 | 12,1 | 12,2 | 13,3 | 16,0 | 19,5 | 23,3 | 24,9 | 24,8 | 22,8 | 19,6 | 16,3 | 13,6 |
| Nea Filadelfeia | 17,6 | 8,7 | 9,3 | 11,2 | 15,3 | 20,7 | 25,6 | 28,0 | 27,4 | 23,3 | 18,1 | 13,7 | 10,3 |
| Rhodes | 19,1 | 11,9 | 12,1 | 13,6 | 16,6 | 20,5 | 24,7 | 26,9 | 27,1 | 24,6 | 20,8 | 16,5 | 13,4 |
| Tatoi | 16,4 | 7,3 | 7,8 | 9,9 | 14,2 | 19,6 | 24,6 | 26,9 | 26,3 | 22,1 | 17,0 | 12,4 | 9,9 |
| Athens (Elliniko) | 18,5 | 10,3 | 10,6 | 12,3 | 15,9 | 20,7 | 25,2 | 28,0 | 27,8 | 24,2 | 19,5 | 15,4 | 12,0 |
| Samos | 18,4 | 10,3 | 10,0 | 12,1 | 15,9 | 20,6 | 25,5 | 28,4 | 27,9 | 24,3 | 19,4 | 14,5 | 11,9 |
| Ierapetra | 19,7 | 12,9 | 12,9 | 14,2 | 17,0 | 20,9 | 25,4 | 27,8 | 27,7 | 24,9 | 21,0 | 17,5 | 14,5 |
| Mytilini | 17,6 | 9,5 | 9,9 | 11,6 | 15,6 | 20,2 | 24,7 | 26,6 | 26,1 | 22,9 | 18,5 | 14,3 | 11,3 |
| Kastoria | 12,9 | 0,5 | 2,7 | 6,7 | 11,6 | 16,8 | 21,0 | 23,1 | 22,5 | 18,4 | 12,6 | 5,0 | 1,2 |
| Grevena | 13,4 | 2,0 | 3,0 | 6,0 | 12,7 | 15,2 | 20,3 | 23,5 | 23,9 | 14,9 | 11,3 | 7,0 | 3,0 |
| Piraeus | 12,35 | 14,5 | 18,1 | 24,4 | 23,5 | 29,1 | 31,5 | 39,2 | 39,1 | 29,0 | 20,1 | 13,0 | 12,7 |
| Oraiokastro | 15,6 | 11,9 | 22,8 | 33,7 | 27,4 | 19,7 | 14,3 | 25,4 | 15,5 | 11,2 | 17,0 | 9,0 | 4,5 |